Summary
Ecology
Life History & Behaviour
Fossil Record
Behaviour
Reproduction and Development
Anatomy & Physiology
Body
Transport, Excretion, Nervous System
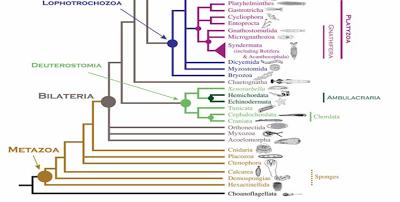
Evolution & Systematics
Phylogeny
Diversification and Classification
Biogeographic Distribution
Conservation & Threats
References & Links | Phylogeny
When those animals were discovered, already in the nineteenth century, they were direct classified as bryozoans, due to their filter- feed sessile life style and the presence of a ‘’crowd” of tentacles on the top. After the increase of studies some differences between those animals were identified, such as the position of the Entoproct anus, differences on cell division processes on embryos phase (spiral cleavage) and the fact that Entoprocts are acoelomate. The most recent conclusion about this group similarity is that they are Trochozoans*, a ‘’superphylum’’ group compost by animals that have a trochophore larvae type.
*Trochozoans:Protostome animals in which the mouth develops first
|
|